

The Global Spine Care Initiative: Care Pathway
Methodology, Contributors, and DisclosuresThis section is compiled by Frank M. Painter, D.C.
Send all comments or additions to: Frankp@chiro.org




FROM: European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 786–795 ~ FULL TEXT
OPEN ACCESS
Claire D. Johnson, Scott Haldeman, Margareta Nordin, Roger Chou, Pierre Côté, Eric L. Hurwitz, Bart N. Green, et. al.
National University of Health Sciences,
Lombard, IL, USA.
globalspinecareinitiative@gmail.com
PURPOSE: The purpose of this report is to describe the Global Spine Care Initiative (GSCI) contributors, disclosures, and methods for reporting transparency on the development of the recommendations.
METHODS: World Spine Care convened the GSCI to develop an evidence-based, practical, and sustainable healthcare model for spinal care. The initiative aims to improve the management, prevention, and public health for spine-related disorders worldwide; thus, global representation was essential. A series of meetings established the initiative's mission and goals. Electronic surveys collected contributorship and demographic information, and experiences with spinal conditions to better understand perceptions and potential biases that were contributing to the model of care.
RESULTS: Sixty-eight clinicians and scientists participated in the deliberations and are authors of one or more of the GSCI articles. Of these experts, 57 reported providing spine care in 34 countries, (i.e., low-, middle-, and high-income countries, as well as underserved communities in high-income countries.) The majority reported personally experiencing or having a close family member with one or more spinal concerns including: spine-related trauma or injury, spinal problems that required emergency or surgical intervention, spinal pain referred from non-spine sources, spinal deformity, spinal pathology or disease, neurological problems, and/or mild, moderate, or severe back or neck pain. There were no substantial reported conflicts of interest.
CONCLUSION: The GSCI participants have broad professional experience and wide international distribution with no discipline dominating the deliberations. The GSCI believes this set of papers has the potential to inform and improve spine care globally. These slides can be retrieved under Electronic Supplementary Material.
KEYWORDS: Global burden of disease; Musculoskeletal system; Quality of health care; Spinal disorders
From the FULL TEXT Article:
Introduction
Reporting transparency in research is imperative, especially as this relates to a consensus process that makes recommendations for the management of important high impact health disorders in low- and middle-income countries. A group of experts may exert undue influence on policies and healthcare decisions; therefore, it is especially important to be transparent about the consensus process and to describe the qualifications, possible biases, and conflicts of interest of each participant. [1–5] Based on the assumption that no author is free from potential bias or conflicts of interest, reporting of conflicts and biases and providing transparency are important to any policy maker, government agency, or institutions attempting to interpret these recommendations. This is of particular importance when individuals and organizations are attempting to influence health care in impoverished communities or low- and middle-income countries. Of equal importance to policy makers and clinicians who are instituting these recommendations is a description of the methodology used to develop the recommendations. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is to report information about the GSCI team participants and their disclosures and to provide a general overview of the methodology used to develop the recommendations.
Methods
This article provides an overview of the methodology and characteristics of the expert participants of the Global Spine Care Initiative (GSCI) and describes of the expertise, clinical experience, and potential biases and conflicts of interests for each member of the GSCI Task Force.
World Spine Care was established in 2008, and its mission is to improve lives in underserved communities through sustainable, integrated, evidence-based spine care. To fulfill this mission, the World Spine Care leaders wished to develop an evidence-based model of care that could be integrated into healthcare programs and implemented anywhere in the world. Therefore, World Spine Care convened the GSCI to develop such a model.
Funding was provided by the Skoll Foundation that provided a matching grant. To receive the grant, GSCI members participated without any remuneration beyond travel expenses, which satisfied part of the requirement for the matching grant. The NCMIC Foundation provided funding to complete the matching requirement. The University of Ontario Institute of Technology-Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College Centre for the Study of Disability Prevention and Rehabilitation received a contract from the GSCI to provide a research librarian and project coordinator as well as first-level reviews of the literature for a number of the scientific papers that make up the proceedings of the GSCI.
The principal investigator (SH) invited co-investigators to form an executive committee. The primary requirement for the executive committee was extensive experience and qualifications in developing evidence-based guidelines and practice parameters for the management of spinal disorders and participation on the executive committee of prior task forces that addressed the management of spine-related complaints. Additional criteria for selecting executive committee members included: primary research or clinical career in spine care; knowledge of current evidence related to spine care; willingness to commit to the GSCI project over a period of 3 years without personal compensation; and no association with any commercial agency or industry that had financial interests in low- or middle-income countries.
Once the executive committee was selected (RC, MN, PC, EH), they developed a list of additional experts to participate in the development of the GSCI articles and consensus process. The executive committee identified clinicians and scientists from around the world with primary interests and experience in spine care. Special effort was made to identify participants from low- and middle-income countries. However, finding these individuals was challenging since those who have an interest or expertise in spinal disorders and are willing to participate without compensation are rare. Healthcare resources tend to focus on infectious and general health issues, and spinal disorders tend to have very little priority in these countries. The executive committee was pleased to find some participants from low- and middle-income countries and other participants who provided health care in these regions. Participants were invited for geographic, professional, and scientific representation. All participants of the GSCI Task Force were invited to contribute to the GSCI model of care through a modified Delphi consensus process.
A series of meetings were convened in the first year to frame the scope of the project. The first meeting held in Chicago, Illinois (July 2014), outlined the core topic areas. The activities included describing the current global burden of spinal disorders through a comprehensive review of the literature for all types of communities and one to focus on the burden experienced by small communities and individuals since this has often been overlooked. Literature reviews were assigned to identify best practices that could be implemented within a spine care pathway, which included assessments, prevention, and treatments.
A meeting in Toronto, Canada (November 2014), and one in San Jose, California (March 2015), brought team members together to discuss their findings. After the third meeting, the topics and goals for the papers were finalized and the lead authors were designated to conduct their literature reviews and write their articles. After the first set of review papers were completed, additional lead authors drafted an evidence-based model of care based on the findings of the literature reviews and completed consensus processes.
Electronic surveys were delivered to each participant using Survey Monkey (SurveyMonkey Inc., San Mateo, California, USA) to collect competing interest and participant information. Surveys included rating scales, multiple-choice, and open-ended questions to allow the participant to include necessary demographic information (see Online Resource for the survey in Appendix 1). All participants were asked to provide consent to participate to allow their names to be listed as authors on the papers that they contributed to.
The questionnaire included:
Information based upon the International Council of Medical Journal Editors conflict of interest form [6].
Information based upon European Spine Journal requirements for reporting funding, bias, conflict of interest, or contributorship.
Demographic and descriptive information about each participant (e.g., degrees, training, discipline, experiences relevant to the project).
Experience with spinal conditions personally or by a family member.
The National University of Health Sciences Institutional Review Board approved this study (#H-1503). All authors were informed and provided their consent to participate.
Results
The GSCI Task Force developed a methodology to establish consensus for the position statements and recommendations in the following areas.
Describe the burden of disease associated with spinal disorders at both the global and community levels.
Define best practices and evidence-based recommendations for patients with spine-related symptoms including assessment, management in the areas of psychological and social, self-care, noninvasive, invasive procedures, and community-based and public health interventions.
Develop a classification system that separates patients with spinal pain syndromes from those likely to have neurological deficits or severe pathology and to differentiate subclasses based on differences in the interventions that are most likely to be beneficial.
Develop an evidence-based care pathway that standardizes how people with spine-related concerns should be managed.
Define the resources necessary to implement the model of care.
Develop and describe an implementable, sustainable, evidence-based model of care that has the capacity to manage the entire spectrum of spine-related disorders; the model of care is based on the results of the literature reviews, the classification, care pathway, and resource lists.
Papers [7–20] were drafted to address these issues and are included in Tables 1 and 2 in the supplemental file (see Online Resource Tables 1 and 2)
Participants
Sixty-eight clinicians and scientists agreed to participate in the deliberations and serve as authors of one or more of the articles that make up the final GSCI report. See Online Resource Table 3 for the reported conflicts of interest and disclosures from all GSCI authors.
The participants were asked to report the nature of their regular occupation and the percentage of time spent on different duties in their full-time jobs: The results were as follows: research 31%, clinical practice 32%, teaching 15%, administrative 17%, industry 1%, and other 4%. (n = 67, one person declined to provide information).
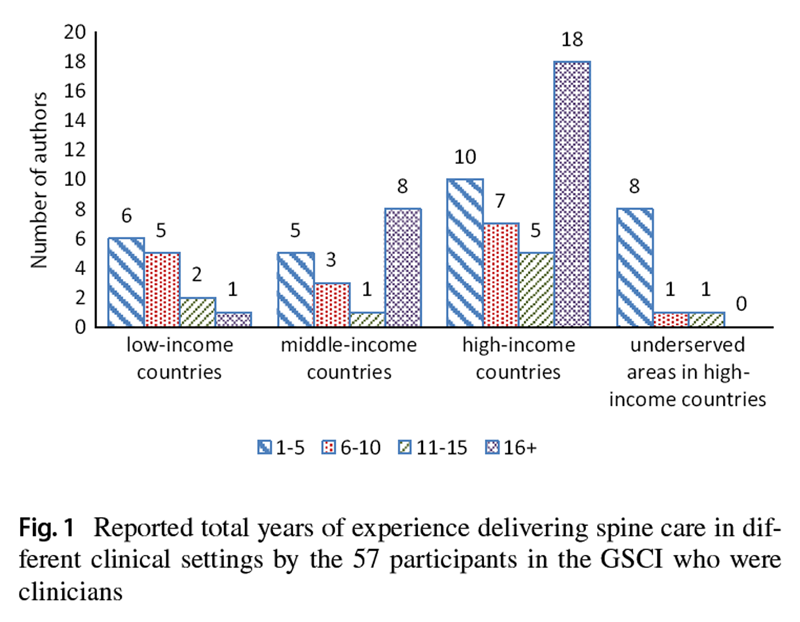
Figure 1
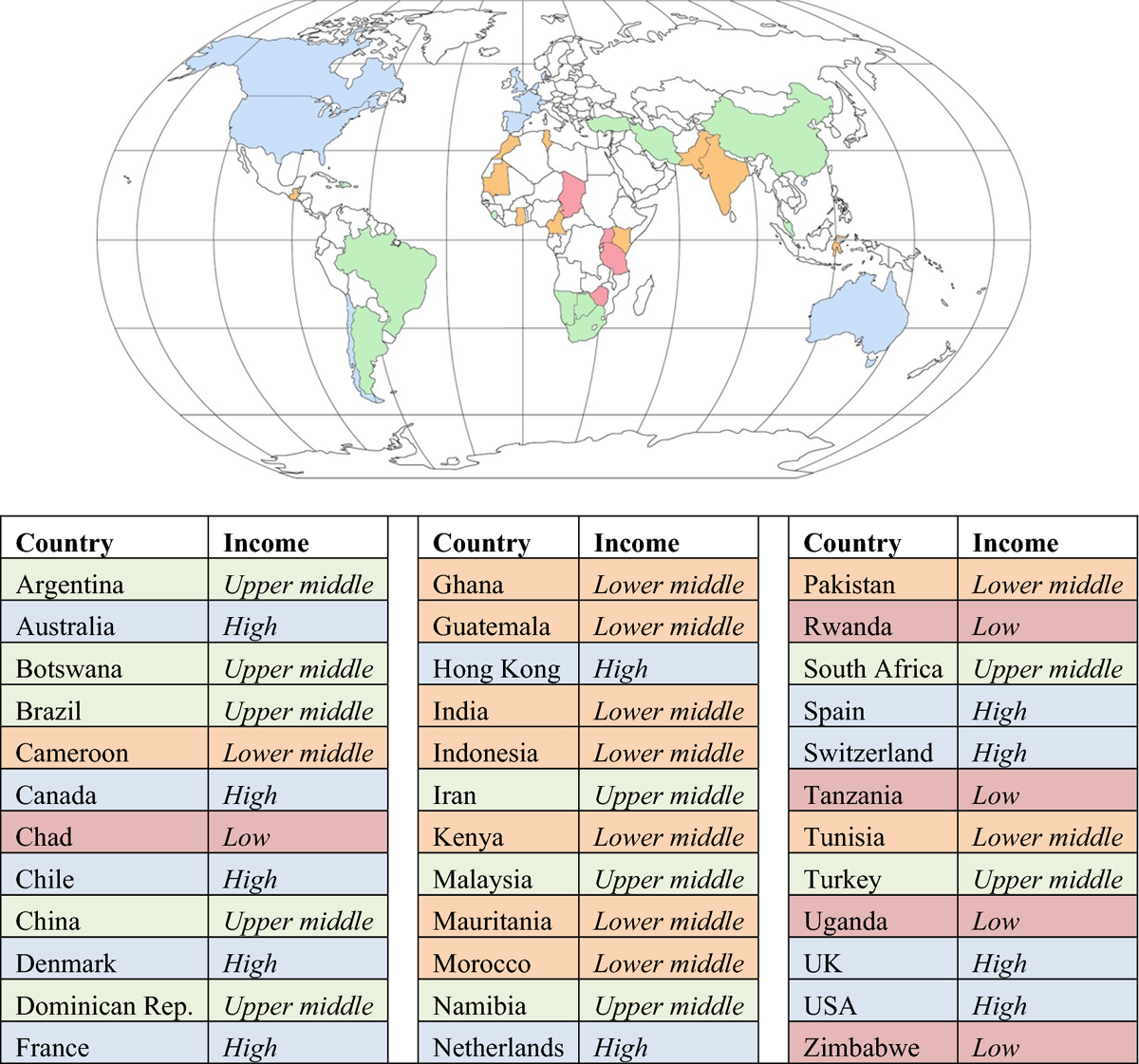
Figure 2
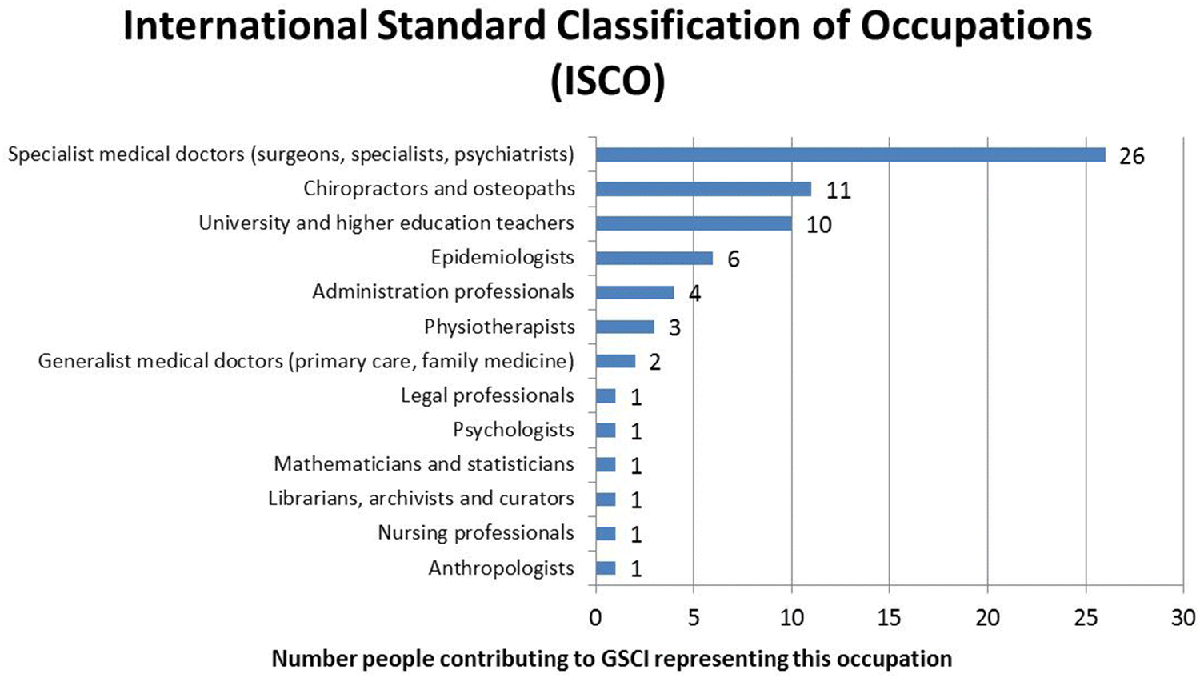
Figure 3
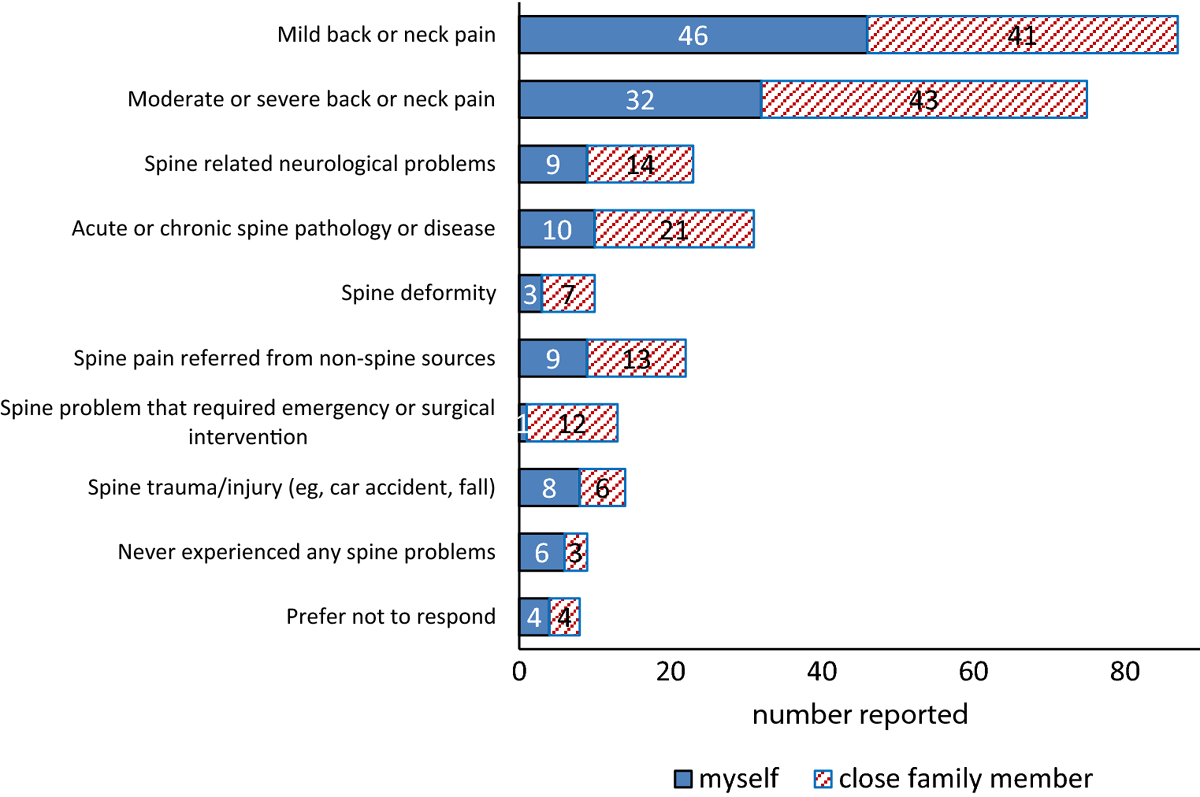
Figure 4 Of the 68 experts, 57 reported having served in clinical practice and providing spine care (one person declined to provide information, ten were not clinical practitioners). The number of years the 57 clinicians provided spine care in low-, middle-, and high-income countries as well as underserved communities in high-income countries is provided in Figure 1.
Countries represented by the GSCI participants
The 68 participants reported 24 countries of current affiliation: Argentina, Australia, Botswana, Brazil, Cameroon, Canada, Chile, Denmark, France, Ghana, India, Iran, Kenya, Malaysia, Morocco, Namibia, Norway, Pakistan, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, Turkey, UK, and USA. The experts reported which countries they had provided spine care at some point in their career, and 36 countries were reported by 57 participants (see Figure 2). Country income level is designated according to the World Bank list of economies as of June 2017 (datahelpdesk.worldbank.org). The GSCI authors reported that they represented 13 different professions according to International Standard Classification of Occupations (see Figure 3).
Personal experience with spine-related concerns by participants of the GSCI
The GSCI authors reported their personal experiences with spine-related conditions. This provided disclosure regarding any perceptions and potential biases that could contribute to the model of care. Information on personal experience with spinal disorders was also used as a proxy for patient input in the GSCI deliberations. Authors were asked whether either they or close family members (e.g., parent, siblings, spouse/partner, and children) had ever experienced any spine-related condition as they related to categories within the GSCI classification system. (see Figure 4) Responses for type of care that either they or their family members received for spine-related concerns ranged from self-care to invasive care, including self-care (e.g., exercise, yoga, ergonomics, postural changes), analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, massage, chiropractic care, physical therapy care, medical care, acupuncture, medical specialty care (e.g., pain clinic, neurologist, orthopedist), surgery.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this project convened the largest number of interprofessional spine experts dedicated to creating a global model of care to reduce the burden of spinal disorders. The number of participants and their variety of disciplines and international distribution provided a broad range of experiences and strengthened the output of this project.
We have done our best to address many of the concerns and comments regarding the development of recommendations. [21–25] The GSCI author team attempted to balance potential biases as much as possible during the deliberations, paper development, and in the determination of recommendations. [7–20, 26] Participants were asked to declare any potential conflicts. There were no substantial commercial or financial conflicts of interest reported by any of the participants and there was no outside commercial entity that could be considered to impact the deliberations. Because a large number of participants provided input into the recommendations, it is proposed that any one particular person’s conflicts would have been diluted.
Adherence to published evidence of spine-related interventions was addressed by including a robust representation from the scientific spine community. The scientific participants included those with experience in epidemiology and public health academic leaders, many of whom had published clinical trials and have been leaders in the development of clinical guidelines for the management of spinal disorders. Additional input was gained through the inclusion of higher education teachers and administrators and an anthropologist.
To address a concern often raised by clinicians that guidelines and health policy do not seem to relate to the real world, patient care environment, we insured that the majority (over 80%) of participants were in either full-time or part-time active clinical practice. Furthermore, the concern that one professional discipline could dominate discussion over another was overcome by ensuring a diverse representation that included most medical and surgical specialties as well as other healthcare providers who focus on spinal disorders from the chiropractic, physical therapy, psychology, and nursing professions.
We tried to diminish including input only from the academic community in high-income countries by ensuring there was representation by participants with experience working in middle- and low-income environments. One-third of the GSCI participants were working in low- and middle-income countries, and almost 50% reported having some experience in such clinical settings. The 24 countries provided representation from five continents.
To make sure that the interests of patients would be taken into account was assisted by recognizing that the majority of GSCI participants or their immediate families had experienced spine-related symptoms and had sought care. The nature of the symptoms or concerns and the healthcare interventions that had been sought by participants was across the range of spinal disorders that the GSCI was attempting to address.
Limitations
The limitations included the absence of lay patients, government health administrators, and payers. We also recognize that more stakeholders from low- and middle-income countries would have been beneficial. Greater representation in these areas may have influenced the deliberations. It was challenging to recruit such participants due to the differences in cultures, resources, and beliefs regarding health care in different parts of the world. Experienced spine clinicians and scientists may approach spine care differently from the general public, and this is an acknowledged weakness of the GSCI panel. Future deliberations and updates to the GSCI should include an even broader representation of stakeholders.
Conclusion
The 68 participants of the GSCI have a comprehensive professional, scientific, and international distribution with no single profession or discipline dominating the deliberations or outcomes. There were no significant financial or commercial conflicts of interest reported.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Funding
The Global Spine Care Initiative and this study were funded by grants from the Skoll Foundation and NCMIC Foundation. World Spine Care provided financial management for this project. The funders had no role in study design, analysis, or preparation of this paper.
Conflict of interest
CDJ is president of Brighthall Inc; she is an NCMIC Board of Director, however, neither she nor NCMIC board makes funding decisions for the NCMIC Foundation; the views in this article are those of the authors and not those of Stanford University, Stanford Health Care, or Qualcomm.SH declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation, NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care. Clinical Policy Advisory Board and stock holder, Palladian Health. Advisory Board, SpineHealth.com. Book Royalties, McGraw Hill. Travel expense reimbursement—CMCC Board. MN declares funding from Skoll Foundation and NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care; Co-Chair, World Spine Care Research Committee. Palladian Health Clinical Policy Advisory Board member. Book Royalties Wolters Kluwer and Springer. Honoraria for speaking at research method courses. RC declares funding from AHRQ to conduct systematic reviews on treatments for low back pain within last 2 years and honoraria for speaking at numerous meetings of professional societies and nonprofit groups on topics related to low back pain (no industry sponsored talks). PC is funded by a Canada Research Chair in Disability Prevention and Rehabilitation at the University of Ontario Institute of Technology and declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation, NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care, Canadian Institutes of Health Research Canada, Research Chair Ontario Ministry of Finance, Financial Services Commission of Ontario, Ontario Trillium Foundation, ELIB Mitac, Fond de Recherche and Sante du Quebec. EH declares he is a consultant for: RAND Corporation; EBSCO Information Services; Southern California University of Health Sciences; Western University of Health Sciences Data and Safety Monitoring Committee, chair, Palmer Center for Chiropractic Research, and research committee co-chair, World Spine Care. BNG receives speaker fees and travel reimbursement from NCMIC Speakers’ Bureau; he is secretary of Brighthall Inc; the views in this article are those of the authors and not those of Stanford University, Stanford Health Care, or Qualcomm.DKG declares travel expenses: CMCC to present at the WSC Spine Conference in Botswana. KR declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation, NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care. EAc declares grants: Depuy Synthes Spine, Medtronic; Speaker’s bureau: AOSpine, Zimmer Biomet. EA declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation, NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care. TB declares European Spine Journal provided a grant to investigate scoliosis. OB declares he is a consultant for: Pacira Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Palladian Health; travel expenses: World Spine Care; and stipend: World Spine Care. PB declares contribution to salary for Global Musculoskeletal Alliance (G-MUSC), The Bone and Joint Decade work. JMC declares funding from Spanish Government Grant ESPY 112/18. SE is an employee of the Botswana Ministry of Health and Wellness. CG declares travel expenses: Palmer College to GSCI meetings, is consultant: American Chiropractic Association, Spine IQ , Healthwise, Quality Insights of Pennsylvania, RAND Co.; Prezacor, Inc. (Stock Options), PCORI (Board Member), and grants: Collaborative Care for Veterans with Spine pain and Mental Health Issues. NIH/ Kiernan Chiropractic Care in Rehabilitation at Crotched Mountain: Crotched Mountain Private Sector Integrated Chiropractic Study N/A. NCMIC Foundation Chiropractic services, Assessment of Chiropractic Treatment for Low Back Pain; RAND Subcontract, Department of Defense Prime Award #W81XWH-11-2-017 Sub #9920110071. JH declares his research group has extensive funding from Danish public funding agencies, the European Union, and Danish charities. MH declares travel support from World Spine Care. JM declares general research resources from USF Research Center, research grants from funding agencies: FEMA, US Department of Homeland Security (EMW-2013-FP-00723), Palladian Health Advisory board: Clinical Policy and Advisory Board, Intellectual property rights: inventor of Web-based system to deliver exercise (Employer—USF: copyright holder). TM declares fellowship grant-Medtronics. JM declares WSC Board Member. EM declares AO Spine Africa Faculty courses - honorarium. GO declares he is a consultant and receives travel support as clinic director, World Spine Care. HR declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation, NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care. MS declares he is a scientific advisor, NuSpine; consultant, and State Farm. ES declares funding from Ba?kent University Research Fund. ATV declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation, NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care. LV declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation and NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care. WW declares Palladian Health Clinical Policy Advisory Board member. JW declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation, NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care. HY declares funding to UOIT from Skoll Foundation, NCMIC Foundation through World Spine Care, and the remaining authors have no conflict of interest.
References:
Norris SL, Holmer HK, Ogden LA, Burda BU (2011)
Conflict of interest in clinical practice guideline development: a systematic review.
PLoS ONE 6(10):e25153Schofferman JA, Eskay-Auerbach ML, Sawyer LS, Herring SA, Arnold PM, Muehlbauer EJ (2013)
Conflict of interest and professional medical associations:
the North American Spine Society experience.
Spine J 13(8):974–979Minter RM, Angelos P, Coimbra R, Dale P, de Vera ME, Hardacre J et al (2011)
Ethical management of conflict of interest:
proposed standards for academic surgical societies.
J Am Coll Surg 213(5):677–682Kirkpatrick JN, Kadakia MB, Vargas A (2012)
Management of conflicts of interest in cardiovascular medicine.
Prog Cardiovasc Dis 55(3):258–265Norris SL, Holmer HK, Burda BU, Ogden LA, Fu R (2012)
Conflict of interest policies for organizations producing
a large number of clinical practice guidelines.
PLoS ONE 7(5):e37413Drazen JM, de Leeuw PW, Laine C, Mulrow C, DeAngelis CD, Frizelle FA et al (2010)
Toward more uniform conflict disclosures–the updated ICMJE reporting
form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest.
Rev Med Chil 138(7):801–803Acaroglu E, Mmopelwa T, Yuksel S, Ayhan S, Nordin M, Randhawa K et al (2017)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: a consensus process to develop and validate
a stratification scheme for surgical care of spinal disorders as
a guide for improved resource utilization in low- and
middle-income communities.
Eur Spine J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-017-5332-zAcaroglu E, Nordin M, Randhawa K, Chou R, Cote P, Mmopelwa T et al (2018)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: A Summary of Guidelines on Invasive
Interventions for the Management of Persistent and Disabling
Spinal Pain in Low- and Middle-income Communities
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 870–878Ameis A, Randhawa K, Yu H, Cote P, Haldeman S, Chou R et al (2017)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: a review of reviews and recommendations
for the non-invasive management of acute osteoporotic vertebral
compression fracture pain in low- and middle-income communities.
Eur Spine J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-017-5273-6Chou R, Baisden J, Carragee EJ, Resnick DK, Shaffer WO, Loeser JD (2009)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: A Narrative Review of Psychological
and Social Issues in Back Pain in Low- and Middle-income Communities
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 823–837Chou R, Cote P, Randhawa K, Torres P, Yu H, Nordin M et al (2017)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: Applying Evidence-based Guidelines
on the Non-invasive Management of Back and Neck Pain to Low-
and Middle-income Communities
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 851–860Green BN, Johnson CD, Haldeman S, Kane EJ, Clay MB, Griffith E et al (2018)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: Public Health and Prevention Interventions
for Common Spine Disorders in Low- and Middle-income Communities
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 838–850Haldeman S., Johnson C.D., Chou R. et al.
The Global Spine Care Initiative:
Classification System for Spine-related Concerns
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 889–900Haldeman S, Johnson CD, Chou R, Nordin M, Côté P, Hurwitz EL et al.
The Global Spine Care Initiative: Care Pathway for People
With Spine-related Concerns
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 901–914Haldeman S, Nordin M, Chou R, Côté P, Hurwitz EL, Johnson CD, Randhawa K et al
The Global Spine Care Initiative: World Spine Care Executive Summary
on Reducing Spine-related Disability in Low-
and Middle-income Communities
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 776-785urwitz EL, Randhawa K, Torres P, Yu H, Verville L, Hartvigsen J et al (2017
The Global Spine Care Initiative: a systematic review of individual
and community-based burden of spinal disorders in rural
populations in low- and middle-income communities.
Eur Spine J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-017-5393-zHurwitz EL, Randhawa K, Yu H, Cote P, Haldeman S (2018)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: A Summary of the Global Burden
of Low Back and Neck Pain Studies
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 796–801Johnson CD, Haldeman S, Chou R, Nordin M, Green BN, Côté P, Hurwitz EL et al (2018)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: Model of Care and Implementation
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 925–945Kopansky-Giles D, Johnson CD, Haldeman S, Chou R, Côté P, Green BN, Nordin M et al (2018)
The Global Spine Care Initiative:
Resources to Implement a Spine Care Program
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 915–924Nordin M, Randhawa K, Torres P, Yu H, Haldeman S, Brady O et al (2018)
The Global Spine Care Initiative: A Systematic Review for the Assessment
of Spine-related Complaints in Populations with Limited
Resources and in Low- and Middle-income Communities
European Spine Journal 2018 (Sep); 27 (Suppl 6): 816–827Raine R, Sanderson C, Black N (2005)
Developing clinical guidelines: a challenge to current methods.
BMJ 331(7517):631Qaseem A, Forland F, Macbeth F, Ollenschläger G, Phillips S, (2012)
Guidelines International Network: toward international
standards for clinical practice guidelines.
Ann Intern Med 156(7):525–531Boivin A, Currie K, Fervers B, Gracia J, James M, Marshall C et al (2010)
Patient and public involvement in clinical guidelines:
international experiences and future perspectives.
BMJ Qual Saf. https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.2009.034835Eccles MP, Grimshaw JM, Shekelle P, Schünemann HJ, Woolf S (2012)
Developing clinical practice guidelines: target audiences, identifying
topics for guidelines, guideline group composition
and functioning and conflicts of interest.
Implement Sci 7(1):60Bakaeen FG, Svensson LG, Mitchell JD, Keshavjee S, Patterson GA, Weisel RD (2017)
The American Association for Thoracic Surgery/Society of Thoracic Surgeons
position statement on developing clinical practice documents.
J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 153(4):999–1005Green BN, Johnson CD, Haldeman S, Griffith E, Clay MB, Kane EJ et al (2018)
A Scoping Review of Biopsychosocial Risk Factors
and Co-morbidities for Common Spinal Disorders
PLoS One. 2018 (Jun 1); 13 (6) :e0197987
Return to GLOBAL BURDEN OF DISEASE
Since 5-14-2020


| Home Page | Visit Our Sponsors | Become a Sponsor |
Please read our DISCLAIMER |
