

Motion Palpation Used as a Postmanipulation Assessment
Tool for Monitoring End-Feel Improvement:
A Randomized Controlled Trial
of Test ResponsivenessThis section is compiled by Frank M. Painter, D.C.
Send all comments or additions to: Frankp@chiro.org




FROM: J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2009 (Sep); 32 (7): 549–555 ~ FULL TEXT
Ekta Lakhani, M TechChiro • Brian Nook, DC • Mitchell Haas, DC, MA • Aadil Docrat, M TechChiro
Chiropractic Department,
Durban University of Technology,
Kwazulu Natal, South Africa.
ektal@dut.ac.za
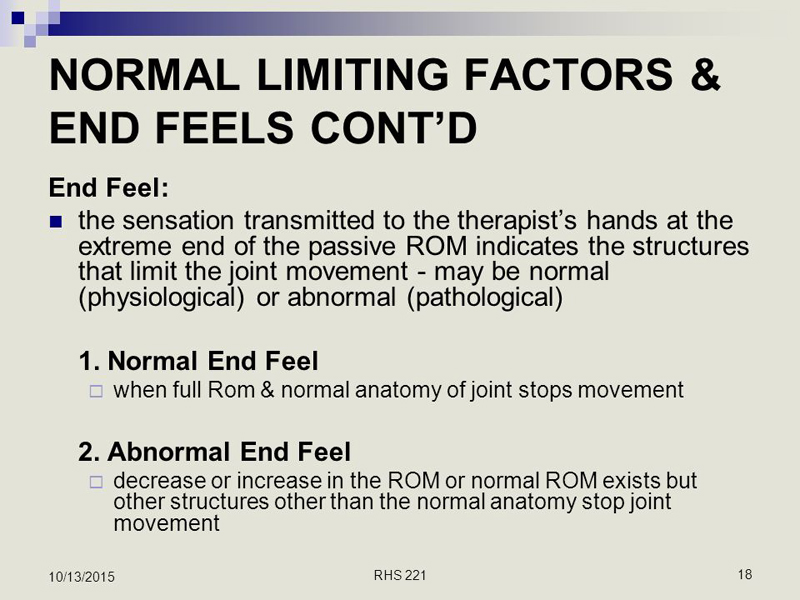
OBJECTIVE: A tenet of motion palpation theory is the ability to confirm postadjustive segmental end-feel improvement (EFI). Only one previous trial has evaluated the responsiveness of EFI; this was a study of the thoracic spine. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the responsiveness of postadjustive end-feel for evaluating improvement in putative segmental spinal motion restriction after spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) of the cervical spine.
METHODS: A prospective, blinded, randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial was conducted with 20 symptomatic and 10 asymptomatic participants recruited from a chiropractic teaching clinic. The treatment group received SMT, and the control group received placebo detuned ultrasound. Responsiveness was evaluated as the etiologic fraction (% of cases with EFI attributable to SMT) and as the sensitivity and specificity of change.
RESULTS: For the entire sample, the etiologic fraction was 63% (P = .002), sensitivity was 93%, and specificity was 67%. For symptomatic participants, a strong relationship appeared to exist between receiving SMT and EFI (etiologic fraction = 78%, P = .006; sensitivity = 90%; specificity = 80%). A strong relationship was not found for asymptomatic participants (etiologic fraction = 40%, P = .444; sensitivity = 100%; specificity = 40%), where EFI was recorded frequently, whether participants received SMT or detuned ultrasound.
There are more articles like this @ our:
LOCATING SUBLUXATIONS PageCONCLUSION: The findings of this study showed that motion palpation of end-feel assessment appears to be a responsive postmanipulation assessment tool in the cervical spine for determining whether perceived motion restriction found before treatment improves after SMT. This observation may be limited to symptomatic participants.

Return to SPINAL PALPATION
Return to LOCATING SUBLUXATIONS
Since 1-16-2019


| Home Page | Visit Our Sponsors | Become a Sponsor |
Please read our DISCLAIMER |