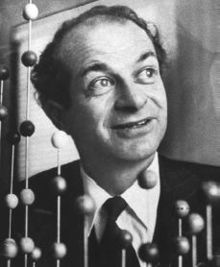The Nutrition Page provides non-solicitous nutrition information, including articles
and research abstracts, supporting the benefits of vitamins, minerals and herbals for
the restoration and maintenance of health. You'll also find links to other useful web sites.





This section was compiled by Frank M. Painter, D.C.
Send all comments or additions to: Frankp@chiro.org
If there are terms in these articles you don't understand, you can get a definition from the Merriam Webster Medical Dictionary. If you want information about a specific disease, you can access the Merck Manual. You can also search Pub Med for more abstracts on this, or any other health topic.
| Jump to: | Supplements | Articles of Interest | The Opinion Section |
|
|
Helpful Tools | Nutrition Links | SEARCH Nutrition |




|
|
Conditions That Respond | Alternative Medicine Approaches to Disease |




Supplement Research




The Supplement section contains information about the characteristics of some of my favorite herbal and dietary supplements. Please note that although these articles and abstracts discuss the relationship between nutritional status and disease, that the Nutrition section is not intended as a prescriptive recommendation for our readers.
Please read our Nutrition Disclaimer.
Please refer to the NIH's Fact Sheets on Dietary Supplements.
The Supplement Section
Acidophilus Pre/Probiotics
Alfalfa
Alpha–lipoic Acid
Antioxidants
Ashwagandha
Bacopa monniera
Banaba Leaf
Bioflavonoids
Black Cohosh
Boswellia serrata
Calcium
Carotenoids
Chromium
Coenzyme - Q10
Echinacea
Fiber
Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA)
Garlic
Ginger
Gingko biloba
Ginseng
Glucosamine
Guaraná Seed Extract
Leucine
Magnesium
Milk Thistle
Nutrient Depletion Charts
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Polyphenols
Phytoalexins
Resveratrol
Saw Palmetto
Selenium
Soy Protein
St. John's Wort
Sterols and Stanols
Vinpocetine
Vitamin B Complex
Vitamin C
Vitamin D
Vitamin E
ZincCondition Specific Nutrition
Alzheimer's and Nutrition
Cancer and Nutrition
Chronic Pain and Nutrition
Immunity and Nutrition
Joint Pain and Nutrition
Memory and Nutrition
Stress and Nutrition
Creatine in Health and DiseaseNutrition and the Complementary Treatment of Disease Enjoy this extensive selection of FULL TEXT articles from the premier complementary medicine journal, Alternative Medicine Review. There are articles here that discuss arthritis, asthma, attention deficit, cancer, chronic fatigue, diabetes, fibromyalgia, hepatitis C, multiple sclerosis, and many other disorders and diseases. Thanks to PubMed for making all these articles available to non-subscribers! Read the Disclaimer
“I believe that you can, by taking some simple and inexpensive measures,
extend your life and your years of well-being.
My most important recommendation is that you take vitamins every day
in optimum amounts, to supplement the vitamins you receive in your food.”
-- Linus Pauling, Ph.D., (1901–1994)
-- Two-time Nobel Prize Laureate




Nutrition Articles of Interest





The Use of Nutritional Guidance Within
~ FULL TEXT
Chiropractic Patient Management
Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2018 (Feb 20); 26: 7
Chiropractors regularly provide nutritional advice and appear to acknowledge the importance of nutrition in their clinical practice especially for patients presenting with chronic disease. If chiropractors are to fulfil their potential in providing such wider public health and preventative health advice to patients, further research examining the utilisation of evidence-based nutrition resources within chiropractic patient management is recommended.

Evidence for Brain Glucose Dysregulation
~ FULL TEXT
in Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimers Dement. 2017 (Oct 19) [Epub]
To the best of our knowledge, this report is the first to measure brain tissue glucose concentrations and assess glycolytic flux to demonstrate their relationships with both severity of AD pathology and the expression of AD symptoms. Including brain tissue samples from “asymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease (ASYMAD)” individuals who represent an intermediate group in the gradation of neuropathology from controls to AD patients in the absence of cognitive impairment during life allowed us to relate measures of brain glucose concentration and glycolytic flux to incremental levels of AD pathology and symptom expression. Equally importantly, by measuring glucose concentrations in brain regions both vulnerable to distinct pathological features of AD, that is, MFG (amyloid deposition) and ITG (tau accumulation) as well as in a region relatively resistant to AD pathology, that is, cerebellum [34], we were able to determine whether the observed alterations in brain glucose concentrations and abnormalities in glycolysis were related to defining pathological processes.

Food Groups and Risk of All-cause Mortality:
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
of Prospective Studies
Am J Clin Nutr. 2017 (Jun); 105 (6): 1462-1473
The associations between 12 food groups defined a priori and risk for all-cause mortality were systematically assessed in this meta-analysis through comparison of extreme categories and dose-response analyses both for linear and nonlinear relations. Nine of the 12 food groups showed an association with all-cause mortality in the categorical or continuous dose-response analyses; an inverse association was present for whole grain, vegetable, fruit, nut, legume, and fish consumption, whereas a positive association was present for red meat, processed meat, egg, and SSB consumption.

The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the
~ FULL TEXT
Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease,
Parkinson's Disease, and Huntington's
Disease: A Mini Review
Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016 (Dec 27); 2016: 8590578
Neurodegenerative diseases affect not only the life quality of aging populations, but also their life spans. All forms of neurodegenerative diseases have a massive impact on the elderly. The major threat of these brain diseases includes progressive loss of memory, Alzheimer's disease (AD), impairments in the movement, Parkinson's disease (PD), and the inability to walk, talk, and think, Huntington's disease (HD). Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are highlighted as a central feature of brain degenerative diseases. Oxidative stress, a condition that occurs due to imbalance in oxidant and antioxidant status, has been known to play a vital role in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases including AD, PD, and HD. A large number of studies have utilized oxidative stress biomarkers to investigate the severity of these neurodegenerative diseases and medications are available, but these only treat the symptoms. In traditional medicine, a large number of medicinal plants have been used to treat the symptoms of these neurodegenerative diseases. Extensive studies scientifically validated the beneficial effect of natural products against neurodegenerative diseases using suitable animal models. This short review focuses the role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of AD, PD, and HD and the protective efficacy of natural products against these diseases.

Genetic Risk, Adherence to a Healthy Lifestyle,
and Coronary Disease
N Engl J Med 2016 (Dec 15); 375 (24): 2349–2358
In conclusion, after quantifying both genetic and lifestyle risk among 55,685 participants in three prospective cohorts and one cross-sectional study, we found that adherence to a healthy lifestyle was associated with a substantially reduced risk of coronary artery disease within each category of genetic risk.

Combining Pain Therapy with Lifestyle: The Role
of Personalized Nutrition and Nutritional
Supplements According to the SIMPAR
Feed Your Destiny Approach
J Pain Res. 2016 (Dec 8); 9: 1179–1189 ~ FULL TEXT
Recently, attention to the lifestyle of patients has been rapidly increasing in the field of pain therapy, particularly with regard to the role of nutrition in pain development and its management. In this review, we summarize the latest findings on the role of nutrition and nutraceuticals, microbiome, obesity, soy, omega-3 fatty acids, and curcumin supplementation as key elements in modulating the efficacy of analgesic treatments, including opioids. These main topics were addressed during the first edition of the Study In Multidisciplinary Pain Research workshop: "FYD (Feed Your Destiny): Fighting Pain", held on April 7, 2016, in Rome, Italy, which was sponsored by a grant from the Italian Ministry of Instruction on "Nutraceuticals and Innovative Pharmacology".
The take-home message of this workshop was the recognition that patients with chronic pain should undergo nutritional assessment and counseling, which should be initiated at the onset of treatment. Some foods and supplements used in personalized treatment will likely improve clinical outcomes of analgesic therapy and result in considerable improvement of patient compliance and quality of life. From our current perspective, the potential benefit of including nutrition in personalizing pain medicine is formidable and highly promising.

Vitamins and Nutrients as Primary Treatments in
Experimental Brain Injury: Clinical Implications
for Nutraceutical Therapies
Brain Res. 2016 (Jun 1); 1640 (Pt A): 114–129
With the numerous failures of pharmaceuticals to treat traumatic brain injury in humans, more researchers have become interested in combination therapies. This is largely due to the multimodal nature of damage from injury, which causes excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, edema, neuroinflammation and cell death. Polydrug treatments have the potential to target multiple aspects of the secondary injury cascade, while many previous therapies focused on one particular aspect. Of specific note are vitamins, minerals and nutrients that can be utilized to supplement other therapies. Many of these have low toxicity, are already FDA approved and have minimal interactions with other drugs, making them attractive targets for therapeutics.
There are more articles like this in our
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Page

Neuroinflammatory Processes in Cognitive
Disorders: Is There a Role for Flavonoids
and N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in
Counteracting Their Detrimental Effects?
Neurochem Int. 2015 (Oct); 89: 63–74
We will also detail the current evidence indicating that flavonoids and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are strong candidates in preventing neuroinflammation and modulating age-related memory decline, and we will describe the potential mechanisms of action underlying their neuroprotective effects. As such, these dietary bioactives represent important precursor molecules in the quest to develop a new generation of drugs capable of counteracting neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases.
There are more articles like this in our
Bioflavonoids Page

Omega-3 Fatty Acids as a Putative Treatment
for Traumatic Brain Injury
J Neurotrauma. 2013 (Jun 1); 30 (11): 897–906
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a global public health epidemic. In the US alone, more than 3 million people sustain a TBI annually. It is one of the most disabling injuries as it may cause motor and sensory deficits and lead to severe cognitive, emotional, and psychosocial impairment, crippling vital areas of higher functioning. Fueled by the recognition of TBI as the “signature injury” in our wounded soldiers in Iraq and Afghanistan, and its often devastating impact on athletes playing contact sports, interest in TBI and TBI research has increased dramatically. Unfortunately, despite increased awareness of its detrimental consequences, there has been little progress in developing effective TBI interventions. Recent evidence, however, strongly indicates that nutritional intervention may provide a unique opportunity to enhance the neuronal repair process after TBI.
There are more articles like this in our
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Page

Get the Lead Out!
MedPage Today (May 13, 2013)
When the FDA finally got around to testing 324 multivitamin-mineral products that target children and pregnant women, they found that only 4 of them were lead-free. [1] Now, new research published in the Pediatrics Journal suggests that even low levels of lead in a supplement can have adverse effects on your children. [2] Why not use a supplement made correctly, so you can protect your family?

Dietary Supplement Recommendations By
Saskatchewan Chiropractors:
Results Of An Online Survey
Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013 (Mar 7); 21 (1): 11 ~ FULL TEXT
All of the respondents (100%) indicated providing nutritional advice or counselling to patients, while nearly all (99%) indicated providing dietary supplement recommendations to patients. Respondents estimated that they provide nutritional advice or counselling to 31% of their patients on average, and recommend dietary supplements to an average of 25% of their patients. The most commonly recommended supplements were glucosamine sulfate, multivitamins, vitamin C, vitamin D, calcium, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics. The most common reasons to recommend dietary supplements were for “general health and wellness” (82% of respondents), “bone health” (74%), “rheumatologic, arthritic, degenerative, or inflammatory conditions” (72%), and “acute and/or chronic musculoskeletal conditions” (65%).

Multivitamins in the Prevention of Cancer in Men:
The Physicians' Health Study II
Randomized Controlled Trial
J American Medical Assoc 2012 (Nov 14); 308 (18): 1871—1880 ~ FULL TEXT
This long-term (11 year) study on the impact of multivitamin supplementation of 14 thousand U.S. physicians revealed that, even with an older population (aged 50-64 years old), supplementation appears to significantly reduce "total cancer incidence", including significantly lower occurrances of prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, and other site-specific cancers.

Nutraceuticals and Their Preventive or Potential
~ FULL TEXT
Therapeutic Value in Parkinson's Disease
Nutrition Reviews 2012 (Jul); 70 (7): 373–386
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common aging-related disorder in the world, after Alzheimer's disease. It is characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta and other parts of the brain, leading to motor impairment, cognitive impairment, and dementia. Current treatment methods, such as L-dopa therapy, are focused only on relieving symptoms and delaying progression of the disease. To date, there is no known cure for PD, making prevention of PD as important as ever. More than a decade of research has revealed a number of major risk factors, including oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Moreover, numerous nutraceuticals have been found to target and attenuate these risk factors, thereby preventing or delaying the progression of PD. These nutraceuticals include vitamins C, D, E, coenzyme Q10, creatine, unsaturated fatty acids, sulfur-containing compounds, polyphenols, stilbenes, and phytoestrogens.

4 Vitamins That Strengthen Older Brains
New Tork Times ~ January 2, 2012
Higher blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B, vitamin C, vitamin D and vitamin E are associated with better mental functioning in the elderly, a new study has found.

Multivitamin and Mineral Supplementation in
1,2-dimethylhydrazine Induced Experimental
Colon Carcinogenesis and Evaluation of
Free Radical Status, Antioxidant
Potential, and Incidence of ACF
Canadian J Physiology and Pharmacology 2012 (Jan); 90 (1): 45–54 ~ FULL TEXT
Researchers publishing in the CJPP found that a diet enhanced with vitamin and mineral supplementation can lower the risk of developing precancerous colon cancer lesions by up to 84%. Colon cancer is the second most common form of the disease affecting men and women in the US, with nearly 150,000 new diagnoses each year.

Why You Should Not Stop Taking Your Vitamins
The Huffington Post (October 20, 2011)
Do vitamins kill people? How many people have died from taking vitamins? Should you stop taking your vitamins? It depends. To be exact, it depends on the quality of the science, and the very nature of scientific research. It is very hard to know things exactly through science. The waste bin of science is full of fallen heroes like Premarin, Vioxx and Avandia (which alone was responsible for 47,000 excess cardiac deaths since it was introduced in 1999).

Changing the Pain-Relief Mindset:
Dietary Alternatives to NSAIDs
Dynamic Chiropractic (May 20, 2011)
More than 50 million Americans suffer with chronic pain, accounting for more than 25 million physician visits per year for low back pain alone. [1] The outcome is a nation of people who rely on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for relief. Unfortunately, this is associated with various side effects that can be life-threatening for some. The second leading cause of peptic ulcers is the use of NSAIDs. Concerning ulcer-induced mortality, one third of NSAID / aspirin deaths are associated with low-dose aspirin use, presumably to prevent cardiovascular disease. [2]

Supplemental Niacin Outperforms 2 Leading
Cholesterol-lowering Drugs
Functional Ingredients (November 2009)
When will they ever learn? There is an adage that says always start with the truth because you will eventually end up there. Such is the case with the recent findings presented at the American Heart Association annual scientific meeting. In case you missed it, the niacin based drug Niaspan outperformed not one, but two, leading cholesterol-lowering drugs: Merck's Zetia, and sister drug Vytorin. Apparently Zetia and Vytorin do little to reduce LDL cholesterol and even less to flush out artery build up.
The “Cure-All Juice” Series

We've all heard the expression that “if it's too good to be true, then it probably isn't”. Well, the makers of various “cure-all juices” lay claim to an astounding assortment of health benefits, with virtually no clinical trials to support them.
Enjoy this series of articles by Douglas Andersen, DC, DACBSP, CCN.
Cure-All Juices, Part 1 ~ Acai and Goji
Cure-All Juices, Part 2 ~ Noni
Cure-All Juices, Part 3 ~ Mangosteen
Cure-All Juices, Part 4 ~ Indian Gooseberry (Amalaki)

Older Adults Who Use Vitamin/Mineral
Supplements Differ from Nonusers
in Nutrient Intake Adequacy
and Dietary Attitudes
J Am Diet Assoc. 2007 (Aug); 107 (8): 1322–1332
A large proportion of older adults do not consume sufficient amounts of many nutrients from foods alone. Supplements compensate to some extent, but only an estimated half of this population uses them daily. These widespread inadequacies should be considered when developing recommendations for supplement use for clients in this age group. Modifying dietary attitudes may result in a higher rate of supplement use in this at-risk population.

Low Vitamin D Levels Common
in Apparently Healthy Girls
Medscape Family Medicine (August 4, 2006)
In a study of healthy adolescent girls, subclinical hypovitaminosis D was a relatively common finding, with non-white girls more severely affected. According to the UK-based study team, “reduced sunshine exposure rather than diet explained the difference in vitamin D status of white and non-white girls” in the study. “Vitamin D deficiency during childhood and adolescence,” warn Dr. M. Zulf Mughal and colleagues in the July issue of the Archives of Disease in Childhood, “might impair the acquisition of peak bone mass at the end of skeletal growth and maturation, thereby increasing the risk of osteoporotic fracture later in life.”

Heavy Metal Content of Ayurvedic
Herbal Medicine Products
JAMA 2004 (Dec 15); 292 (23): 2868–2873
It's long been known that certain Chinese herbal medicines contain potentially dangerous metals, but no one has determined whether Ayurvedic supplements pose the same problem. This Harvard study looked at Indian Ayurvedic herbs, and the news is not good. Researchers at Harvard bought 70 Ayurvedic products, nearly all of them made in India, and found that one in five contained potentially harmful levels of lead, mercury, and arsenic.

Flawed Meta-Analysis Misrepresents
Vitamin E Research
November 16, 2004 –– A flawed "retrospective review" published in the Annals of Internal Medicine took a narrow look at only 19 of the more than 2,170 published papers addressing the efficacy and safety of Vitamin E. Strangely, "18 of those 19 clinical studies showed no increase in the risk for health complications or fatalities with Vitamin E versus a control group. Only one study out of the 19 demonstrated a higher risk and that study was with patients who were using estrogen hormone replacement therapy (HRT) along with Vitamin E."

Health Care For Our Bones: A Practical
Nutritional Approach to
Preventing Osteoporosis
J Manipulative Physiol Ther 2004 (Nov); 27 (9): 591–595 ~ FULL TEXT
When patients and doctors think of osteoporosis, calcium immediately comes to mind. “Bones contain calcium, and, therefore, take calcium to protect your bones,” is the battle cry that we hear most often from doctors, government agencies, and media sources. This commentary will provide a story of osteoporosis beyond calcium, which is one that practitioners and researchers need to consider when treating or investigating this pervasive condition.

Nutritional Alternatives for Statin Drugs
American Chiropractor 2004 (Sep); 26 (6) ~ FULL TEXT
A USAToday.com article, posted on June 8, 2004, stated that, “Bayer pulled Baycol after reports that 31 people taking the drug died of a rare but dangerous side effect called rhabdomyolysis, a toxic breakdown of muscle tissue that can lead to kidney failure. All statins have been associated with muscle problems, most of them not fatal, and patients are warned to report to their doctors any symptoms such as muscle pain, weakness, fatigue, dark urine, nausea and vomiting.” We need to focus on the statement that, “All statins have been associated with muscle problems.” In fact, muscle pain is very common in those taking statins. Long term use of statins is known to substantially increase the risk of developing polyneuropathy in some patients. [1] Statins also commonly cause fatigue [2] and memory loss and cognitive defects. [3] Severe irritability and aggression have also been attributed to statin use. [4]

The Role of Chronic Inflammation in
Cardiovascular Disease and its
Regulation by Nutrients
Alternative Medicine Review 2004 (Mar); 9 (1): 32–53 ~ FULL TEXT
Nutrients such as arginine, antioxidants (vitamins C and E, lipoic acid, glutathione), and enzyme cofactors (vitamins B2 and B3, folate, and tetrahydrobiopterin) help to elevate nitric oxide levels and may play an important role in the management of cardiovascular disease. Other dietary components such as DHA/EPA from fish oil, tocotrienols, vitamins B6 and B12, and quercetin contribute further to mitigating the inflammatory process.

Nutrients and Botanicals for Erectile Dysfunction:
Examining the Evidence
Alternative Medicine Review 2004 (Feb); 9 (1): 4–16 ~ FULL TEXT
A review of the available empirical evidence reveals most naturally occurring compounds lack adequate clinical trials to support efficacy. However, arginine, yohimbine, Panax ginseng, Maca, and Ginkgo biloba all have some degree of evidence they may be helpful for erectile dysfunction.

Nutritional Support for Wound Healing
Alternative Medicine Review 2003 (Nov); 8 (4): 359–377 ~ FULL TEXT
Healing of wounds, whether from accidental injury or surgical intervention, involves the activity of an intricate network of blood cells, tissue types, cytokines, and growth factors. This results in increased cellular activity, which causes an intensified metabolic demand for nutrients. Nutritional deficiencies can impede wound healing, and several nutritional factors required for wound repair may improve healing time and wound outcome.

Hot Flashes: A Review of the Literature on
Alternative and Complementary
Treatment Approaches
Alternative Medicine Review 2003 (Aug); 8 (3): 284–302 ~ FULL TEXT
Hot flashes are a common experience for menopausal women, with an 85-percent incidence in the West. With the increased knowledge of side effects attributable to conventional treatment options, more women are exploring natural alternatives. Although more definitive research is necessary, several natural therapies show promise in treating hot flashes without the risks associated with conventional therapies. Soy and other phytoestrogens, black cohosh, evening primrose oil, vitamin E, the bioflavonoid hesperidin with vitamin C, ferulic acid, acupuncture treatment, and regular aerobic exercise have been shown effective in treating hot flashes in menopausal women.

Outcome-based Comparison of Ritalin versus
Food-supplement Treated Children with ADHD
Alternative Medicine Review 2003 (Aug); 8 (3): 319–330 ~ FULL TEXT
Numerous studies suggest that biochemical heterogeneous etiologies for AD/HD cluster around at least eight risk factors: food and additive allergies, heavy metal toxicity and other environmental toxins, low-protein/high-carbohydrate diets, mineral imbalances, essential fatty acid and phospholipid deficiencies, amino acid deficiencies, thyroid disorders, and B-vitamin deficiencies. The dietary supplements used were a mix of vitamins, minerals, phytonutrients, amino acids, essential fatty acids, phospholipids, and probiotics that attempted to address the AD/HD biochemical risk factors. These findings support the effectiveness of food supplement treatment in improving attention and self-control in children with AD/HD and suggest food supplement treatment of AD/HD may be of equal efficacy to Ritalin treatment.
You may also want to refer to our
ADD/ADHD Page

Can Vitamins Decrease The Risk
of Women's Cancers?
Functional Foods & Nutraceuticals (June 2003)
Recent randomised controlled trials of supplements have yielded some unexpected findings. In trials of high-risk individuals (smokers or asbestos workers), beta-carotene, which had been believed to prevent cancer, was found to actually increase the incidence of lung cancer, while vitamin E had no effect on lung cancer risk. [1, 2] Selenium, which was hypothesised to reduce risk of non-melenomatous skin cancers, had no effect on skin cancer, but instead reduced the risk of a broad range of other cancers. [3] A New York Times front page story stated: "Consumers are, in effect, volunteering for a vast, largely unregulated experiment with substances that may be helpful, harmful or simply ineffective." [4]

Better Nutrition Nets Good Behaviour
Functional Foods & Nutraceuticals (Sepember 2002)
An extended UK study has found that adding vitamins, minerals and other nutritional elements to the diets of young criminals held in custody can help reduce anti-social behaviour and the number of offences they commit. The 18-month long study, on 230 men at a maximum-security institution found that the supplement group committed a quarter fewer offences, with violent offences falling by 40 per cent. There was no drop in offence rates in the control group.

Ginger Alleviates Morning Sickness
Nutrition Science News (July 2001)
Ginger (Zingiber officinale), a commonly used folk remedy, has been confirmed to effectively treat nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. A placebo-controlled, double-blind study of 67 pregnant women with morning sickness was conducted by Teraporn Vutyavanich, M.D., of Chiang Mai University in Thailand. Thirty-two women were given 250 mg of ginger four times daily while 35 received placebo.

Turning the Tables on Drug Interactions
Nutrition Science News (July 2001)
As vitamin supplements and herbal remedies move to the mainstream, health care professionals are closely monitoring the interactions between natural products and drugs. However, understanding such biochemical interactions is no easy task. Vitamins and herbs clearly complicate the existing problems of drug interactions. Medical journals that are addressing vitamin, herb and drug interactions are using the watchword "caution" for those clinicians prescribing natural products in conjunction with pharmaceuticals.

How Nutrients Differ From Drugs
Nutrition Science News (April 2001)
Many physicians use vitamin and mineral supplements to prevent and treat disease. For example, vitamin E reduces coronary artery disease risk, and it can benefit people with confirmed cardiovascular disease. [1] Similarly, selenium supplements reduce some cancer risks [2] and improve the health of AIDS patients. [3] But do large supplemental doses somehow turn nutrients into drugs? I would argue that once a nutrient, always a nutrient.

Enzymes Can Hasten Pain Relief
Nutrition Science News (February 2001)
One of the more common reactions to pathological processes is inflammation. Just about every disease or injury involves some form of it, which often manifests as pain. Enzymes, particularly proteases that break down proteins, can effectively be used to ease inflammation.

Supplementing Vegetarian Diets
Nutrition Science News (October 2000)
Vegetarian diets have blossomed and proliferated far beyond their countercultural roots in the early 1970s. Scientific evidence now makes clear that eliminating meat from the diet can indeed be a healthy choice. In fact, switching to a high intake of plant foods will provide the body with substantial amounts of vitamins, minerals and phytochemicals and low amounts of saturated fat—factors that have been associated with reduced risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease. [1] During the last 30 years, interest in such plant-based diets has shifted from assessing their adequacy to determining their specific health benefits. [2] And although scientists agree that there are a number of advantages, many also feel that, under certain circumstances, vegetarians may not be getting enough of a handful of nutrients.

A Supplement Plan for Seniors
Nutrition Science News (December 1999)
In fact, with current knowledge, older customers can design a supplement program to protect them from the age-related decline that typically occurs among people who do not take care of themselves. The following supplements can be added gradually to their plan as they grow older. Start them with a basic comprehensive multivitamin and mineral with enough B complex; basic amounts of vitamin C and E; beta-carotene; trace minerals including chromium, copper, manganese, selenium and zinc; and, if possible, adequate magnesium and calcium, which may need to be taken separately because of their bulk.

And the Good Herb Taketh Away
Nutrition Science News (October 1999)
Botanical medicines may be safer than pharmaceuticals, but the potential to cause ill effects still exists. Gentle, natural herbs have gained a reputation as being able to do no wrong. Most consumers consider them safe healing agents without the side effects of prescription drugs. And overall, herbs generally are safe when used appropriately in recommended doses. But, as with any medicine, there are points to keep in mind when taking them therapeutically.

Supplements Facts ~ All the Facts:
What the New Label Does And Doesn't Disclose
Alternative Medicine Review 1999 (Feb); 4 (1): 5–9 ~ FULL TEXT
Under "Other Ingredients," just below the Supplement Facts box, you will find additives: Binders (to bind tablets together); Lubricants (to assist powder flow in manufacturing); Coatings (to coat tablets and permit easier swallowing); Colorings (cosmetic reasons); and Fillers (used to fill space). The following is a list of many such additives grouped into general categories relative to their potential to cause allergic or sensitivity reactions, impede absorption, or have an undesired physiological effect.

Vegetarian Children: How Healthy Are They?
Are Their Nutritional Needs Being Met?
Concerned parents who want to raise healthy vegetarian children often ask about their children's specific nutritional requirements. Are they getting enough iron or calcium? Should they be taking supplements? Will they be as strong and grow as fast as their omnivorous friends? These are valid concerns, but all of them can be resolved if parents provide a balanced and varied diet.

Natural Suggestions For Indigestion
Natural Foods Merchandiser (December 2000)
Antacids sold by the gross, travel packs filled with chalky pills and fizzing tablets... Indigestion is universal, and any pharmacy worth its salt devotes an entire aisle to alleviating the nausea, gas and belching associated with it. And that's not counting the prescription antacids and antispasmodics behind the counter. But relief doesn't have to be expensive or come with side effects. Herbs and enzymes offer an easy-to-swallow alternative to that awful full feeling.

Pet Allergies: How To Stop The Scratching
Nutrition Science News (July 1999)
Dogs, and an increasing number of cats, often have seasonal allergies that send their owners scurrying for answers each summer. Although some pets may have weepy eyes and runny noses, the primary sign of allergies is constant scratching. Often, the cause of all this itchy skin is inhaled allergens. In addition, food or contact allergies, infections, skin damage, or conditions such as seborrhea, a disease of the sebaceous glands, can also be involved. The degree of pruritus, or excessive itchiness, is determined by the amount of allergens in the pet's environment, the number of things the pet is allergic to and how many other skin problems the pet has. [1, 2] Veterinarians can perform skin cultures and blood tests to more accurately determine the cause of the itching.

Complementary Treatment for Diseases
A Chiro.Org article collection
Enjoy this extensive selection of FULL TEXT articles from the premier complementary medicine journal, Alternative Medicine Review. There are articles here on arthritis, asthma, attention deficit, cancer, chronic fatigue, diabetes, fibromyalgia, hepatitis C, multiple sclerosis, and many other disorders and diseases. Thanks to PubMed for making all these articles available to non-subscribers! Please read our Disclaimer.

Archives of Our "Older" Nutrition Articles
The Opinion Section
Organic Foods ~
Are They Really Better?

Higher Antioxidant and Lower Cadmium
Concentrations and Lower Incidence of
Pesticide Residues in Organically
Grown Crops: A Systematic
Literature Review and
Meta-analyses
British J Nutrition 2014 (Sep 14); 112 (5): 794–811 ~ FULL TEXT
In the present study, we carried out meta-analyses based on 343 peer-reviewed publications that indicate statistically significant and meaningful differences in composition between organic and non-organic crops/crop-based foods. Most importantly, the concentrations of a range of antioxidants such as polyphenolics were found to be substantially higher in organic crops/crop-based foods, with those of phenolic acids, flavanones, stilbenes, flavones, flavonols and anthocyanins being an estimated.

It's Now Official: Organic Really Is Better
BBC News Report (October 28, 2007)
This article reports on a four-year study, funded by the European Union. A group of researchers grew fruit, vegetables, and reared cattle on adjacent organic and non-organic farms across Europe, including a 725-acre farm attached to Newcastle University in England. They discovered that the organic fruit and vegetables they produced contained 40% more antioxidants than conventional produce. Lab assays of the milk from their organic cattle revealed that the organic milk contained 50% to 80% more antioxidants than their conventional milk. They also found that other organic staples they grew, including wheat, tomatoes, potatoes, cabbage, onions, and lettuce also contained 20% to 40% more nutrients than their conventional counterparts.
You may also enjoy this companion piece, titled:
Organic Produce Is 'Better For You'

Organically Grown Foods: Evaluate Your Options
Mayo Clinic (December 22, 2004)
Most supermarkets carry organic foods, including organic fruits, vegetables, meat and dairy products. There are several differences between organic and nonorganic foods and many factors that might influence your decision to buy – or not buy – these products. Let's review them now.

Organic Food Is More Nutritious
Nutrition Science News (September 2001)
For years, organic food proponents have suspected that organic food is higher in minerals and vitamins than conventionally farmed produce. As part of her doctoral dissertation, Virginia Worthington, Ph.D., of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, reviewed available research comparing the nutritional value of organically grown and conventionally grown produce. She concluded that organic produce is nutritionally superior.

Organic Food “Proven” Healthier
BBC News (January 3, 2000)
Mr. Holden said organic crops also have a measurably higher level of vitamins, and that this can benefit people who eat them. By contrast, he said, "intensive farming is devitalizing our food". Mr. Holden said the research, from Denmark and Germany, would be presented in the UK at the association's conference on organic food on 8 January.

Is Organically Grown Food More Nutritious?
Alternative Therapies Health Med 1998 (Jan); 4 (1): 58–69
The most relevant studies then, are not those that simply assess nutrient content, but are those that feed organic or conventional feed to animals and then look at how healthy they are. There are 14 such animal studies that have been performed over the last 70 years. In ten of these, the organically fed animals fared better; in one, the animals fed organic feed came in second among several chemically fertilized feeds; and 3 studies showed no difference, possibly due to weaknesses in the study designs.

New Organic Food Guidelines Take Effect
New USDA guidelines go into effect on Oct. 21,2002
Prior to the USDA’s new statute, a product sold anywhere in the U.S. with as little as 1 percent of its ingredients comprised of organic material could claim to be an “organic” product to consumers. Now, any product imported from other countries or grown in the U.S. that wants to use the label organic must follow strictly worded guidelines and be free of conventional pesticides, GMOs and radiation.

Are Organics Really Healthier?
Functional Foods & Nutraceuticals (March 2003)
High on the list of consumer food safety concerns are pesticide residues in food. Annual surveys in the UK and US typically reveal that approximately one-third of all conventional food samples and half of all fresh produce tested contain low levels of pesticide residues. Regulators assert that rigorous safety assessments have confirmed that these levels are not a threat to food safety. Consumers intuitively know this is a false assurance. No rigorous scientific safety assessment has or can be made of the infinite number of mixtures of compounds consumers are exposed to. Individual samples sometimes contain up to seven different pesticides, and the US FDA has found up to 350 different pesticides in foods sampled.

Our Food is Becoming Less Nutritious. Why?
Organic Gardening.com
In the April 1943 issue of Organic Farming and Gardening, our visionary founder J.I. Rodale wrote: "The United States Government has admitted that the reason 50 percent of the men called for the draft were rejected was because they were undernourished. Now, all these men ate plenty of food, but this food lacked enough minerals and vitamins to make them physically fit.

What's Behind Your Organic Food?
Better Nutrition
What constitutes an organic product? The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) dictates that organic foods must be produced by farmers who “emphasize the use of renewable resources and the conservation of soil and water to enhance the environmental quality for future generations.” But what this really means varies depending upon the product. Meat, poultry, egg and dairy products must be from animals that are never given synthetic growth hormones or antibiotics. The animals must also be fed an organic diet and be allowed to roam freely. Organic fruits and vegetables may not be grown using any conventional pesticides, nor may the land be treated with synthetic fertilizers or sewer sludge.
That Rarest of Birds: Early Medical Support for Supplementation

Long Maligned Vitamins Now Have
Doctors' Official Stamp of Approval
Seattle Times (July 28, 2002)
The vitamin wars are officially over. Record the date for posterity: June 19, 2002. That's when the American Medical Association published a radical new recommendation - most Americans should be taking vitamins. This discussion is based on the release of the following JAMA article (see it just below).

Vitamins for Chronic Disease Prevention
in Adults: Clinical Applications
JAMA 2002 (Jun 19); 287 (23): 3127–3129 ~ FULL TEXT
Reversing a long-standing anti-vitamin policy, the Journal of the American Medical Association just advised all adults to take at least one multivitamin each day. It now appears that people who get enough vitamins may be able to prevent such common chronic illnesses as cancer, heart disease and osteoporosis, according to Drs. Robert H. Fletcher and Kathleen M. Fairfield of Harvard University , who wrote the journal's new guidelines. The last time the journal prepared a comprehensive review of vitamins, about 20 years ago, it concluded that multivitamins were a waste of time and money. People could get all the nutrients they needed from their diet, it advised. Oh, the times they are 'a changing!

Eat Right and Take a Multivitamin
New England Journal of Medicine 1998 (Apr 9); 338 (15): 1060–1061
Since the mid-1970s, 25 percent of American adults have regularly consumed a multivitamin containing 400 µg of folic acid. The current evidence suggests that people who take such supplements and their children are healthier. This evidence raises the question of whether physicians and other health care professionals should recommend that all adults take a multivitamin daily.
Are Supplements Worth the Money?

Why Not Buy the Cheapest Vitamins?
Quality IS an issue when buying supplements, just like it is an issue when buying carpet or clothes. There are 100's of brands of food supplements on the market, but let's look at some quality issues.

Why Supplements Are Necessary
Renewal: The Anti-Aging RevolutionSt. Martin's Press 1999
I am breaking my "non-commercial-only" tradition by listing this article, from Rodale Presses "Renewal: The Anti-Aging Revolution", which I found on a commercial vitamin-sales website. That's because this chapter is clear, accurate, and easy to understand! Please remember that commercially available vitamins usually haven't been tested for the purity and potency of their raw-materials, the accuracy of their dosage, or their bio-availability once it's inside your digestive tract. The research findings presented in these pages are based on the use of pharmaceutically produced products for that trial, not products available in "health food" stores or at a pharmacy.

Military Program Proposes Saving Money
Through Vitamin E Supplementation
WASHINGTON, May 22, 1997
A 1997 report by the National Defense Council Foundation finds that the federal government could save up to $6.3 billion annually by increasing the health of active and retired military personnel through a anti-aging program that includes the use of vitamin supplementation.
Genetically-modified (GM) Food ~ Is It Safe?

GM Food: Head to Head: Point/Counterpoint
Tuesday, 18 May, 1999
Enjoy this debate between Dr Ian Taylor, the Scientific Political Adviser for Greenpeace, and Clive Rainbird, a Biotechnology Communications Manager for manufacturers AgrEvo.

Genetically Modified Foods Warning
American Academy of Environmental Medicine
Because GM foods pose a serious health risk in the areas of toxicology, allergy and immune function, reproductive health, and metabolic, physiologic and genetic health and are without benefit, the AAEM believes that it is imperative to adopt the precautionary principle, which is one of the main regulatory tools of the European Union environmental and health policy and serves as a foundation for several international agreements. [13] The most commonly used definition is from the 1992 Rio Declaration that states: “In order to protect the environment, the precautionary approach shall be widely applied by States according to their capabilities. Where there are threats of serious or irreversible damage, lack of full scientific certainty shall not be used as a reason for postponing cost-effective measures to prevent environmental degradation.” [13]

How To Avoid Food Brands Made With
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
Institute for Responsible Technology (March 2009)
Genetic Engineering (GE) or Genetic Modification (GM) of food involves the laboratory process of artificially inserting genes into the DNA of food crops or animals. The result is called a genetically modified organism or GMO. GMOs can be engineered with genes from bacteria, viruses, insects, animals, or even humans. Most Americans say they would not eat GMOs if labeled, but unlike most other industrialized countries, the U.S. does not require labeling.
Fad Diets ~ Do They Help?

FTC Takes a Regulatory Sledgehammer
to the Weight Loss Market
NutriSciences Blog (April 27th, 2009)
Weight loss has been the focus of the FTC over the past few years but '08 and '09 have seen a significant step up in their activity. Within the last week we have seen 2 of the heavy weight formulations receive legal attention. In 2005 The FTC charged RTC Research & Development, LLC with making false and unsubstantiated weight-loss claims for Xenadrine EFX. In 2006 the court found in favour of the FTC and under the terms of the settlement RTC to pay $8 million in consumer redress. Most recently the FTC also charged suppliers of Hoodia gordonii, including Nutraceuticals International, Stella Labs, as well as individual defendants from these companies, with deceptive advertising claims. The FTC alleges that the defendants not only made false and deceptive claims about what hoodia could do, but also, claimed that their product was Hoodia gordonii, a plant native to southern Africa, when it was not.

The Trend Diets
Today's Chiropractic (January 2004)
Strictly speaking, our “diet” is whatever we eat. For some years, however, the term has been synonymous with weight loss. It conjured up images of calorie counting, carbohydrate charts, and fat grams, all topped with a helping of discipline, and maybe a lapse or two on the side. Nutrition or health often were meager portions if they were served at all. The goal was to trim the waistline. But increasingly, creators of weight-loss diets present health concerns, e.g. nutrients and exercise, as integral parts of their programs. Likewise, proponents of health-based diets say that achieving proper weight is a natural result of their regimens.

Fad Diets Analyzed
Today's Chiropractic (March 2004)
In this article, we will examine the scientific pros and cons regarding low carbohydrate, high protein diets such as the Atkins and South Beach diets in managing our weight and achieving optimal body composition. In order to understand the principles of weight management, we will first review the basics of Basal Energy Expenditure (BEE) and Total Energy Requirements (TER), which include BEE and energy requirements for external activities. We will then discuss a few tips for safe and permanent weight management.
Helpful Nutrition Tools

Drug-Nutrient Depletion and Interaction Charts
A Chiro.Org article collection
This page included numerous charts from Ross Pelton's Drug-Induced Nutrient Depletion Handbook, along with numerous other articles about which drugs deplete (or block absorption) of key nutrients.

All About Telomeres
A Chiro.Org article collection
Enjoy several videos by Nobel Prize winner Elizabeth Blackburn, and a host of other articles about the length of your telomeres, and the impact that will have on your health and mental state.

Alzheimer's Disease
A Chiro.Org article collection This new collection of articles tracks the various underlying causes of cognitive decline, and the lifestyle changes that appear to improve those symptoms.

Office of Dietary Supplements @ NIH
This National Institutes of Health (NIH) site defines supplements, and contains the
The International Bibliographic Information on Dietary Supplements (IBIDS) Database.
You may also find value with the NCCAM Dietary and Herbal Supplements Page.

The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) On-line
Find out about your food, supplements, drugs, the drugs given to animals (which you are eating indirectly!), cosmetics and a bunch of other stuff! You may also enjoy their Search Page.

The Menopause Relief Page
Review articles and abstracts discussing the benefits of Soy Protein and Black Cohosh for peri-menopausal symptoms and osteoporosis, and the risks of estrogen replacement products.

The Women's Health Page
Review the collection of articles relating to women's health and reproductive issues. There is also a significant "links" section.

Nutrient Depletion Charts
These tables describe what nutrients are depleted with the use of corticosteroids, NSAIDS and other commonly prescribed chemicals.

Show me the Food Guide Pyramid
This contains serving sizes and suggestions for how to make the best choices for you and your family.

The Leading Causes of Death
The leading causes of death are all lifestyle related and often preventable. Chronic diseases comprise the three leading causes of death in the United States -- heart disease, cancer, and cerebrovascular disease -- and they account for nearly two thirds of all deaths.

FDA-Authorized Health Claims
This is a simple table of the 11 FDA “approved” claims for foods and supplements.
Nutrition Links
Nutrition Journals
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism
Annual Review of Nutrition
Clinical Nutrition
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
European Journal of Nutrition
HerbalGram ~ The Journal of the American Botanical Council
Journal of Nutrition
Journal of the American College of Nutrition
Nutrition and Cancer
Nutrition Journal ~ Full Text
Other Reference Materials
The Codex Alimentarius Page
Council for Responsible Nutrition
Herbal Materia Medica (Individual Herbs)
Herb Med Information Page
Herbal Medicine from Medline Plus
The Linus Pauling Institute
Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
Prevention Magazine
School of Botanical Medicine
Contains sketches and photographs of many Herbs and contains several on-line textbooks

Return to the LINKS
Return to WOMEN'S HEALTH
Return to MENOPAUSE RELIEF
Since 5–01–1997
Updated 1–01–2026
29 years online, and still going strong.


| Home Page | Visit Our Sponsors | Become a Sponsor |
Please read our DISCLAIMER |